|
|
PDF MMSF5P02HD Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | MMSF5P02HD | |
| Descripción | SINGLE TMOS POWER MOSFET 8.7 AMPERES 20 VOLTS | |
| Fabricantes | Motorola Semiconductors | |
| Logotipo | ||
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de MMSF5P02HD (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 12 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
MOTOROLA
SEMICONDUCTOR TECHNICAL DATA
™Designer's Data Sheet
Medium Power Surface Mount Products
TMOS Single P-Channel
Field Effect Transistors
MiniMOS™ devices are an advanced series of power MOSFETs
which utilize Motorola’s High Cell Density HDTMOS process. These
miniature surface mount MOSFETs feature ultra low RDS(on) and true
logic level performance. They are capable of withstanding high energy in
the avalanche and commutation modes and the drain–to–source diode
has a very low reverse recovery time. MiniMOS devices are designed for
use in low voltage, high speed switching applications where power
efficiency is important. Typical applications are dc–dc converters, and
power management in portable and battery powered products such as
computers, printers, cellular and cordless phones. They can also be
used for low voltage motor controls in mass storage products such as
disk drives and tape drives. The avalanche energy is specified to
eliminate the guesswork in designs where inductive loads are switched
and offer additional safety margin against unexpected voltage transients. G
• Ultra Low RDS(on) Provides Higher Efficiency and Extends Battery Life
• Logic Level Gate Drive — Can Be Driven by Logic ICs
• Miniature SO–8 Surface Mount Package — Saves Board Space
• Diode Is Characterized for Use In Bridge Circuits
• Diode Exhibits High Speed, With Soft Recovery
• IDSS Specified at Elevated Temperature
• Avalanche Energy Specified
• Mounting Information for SO–8 Package Provided
Order this document
by MMSF5P02HD/D
MMSF5P02HD
Motorola Preferred Device
SINGLE TMOS
POWER MOSFET
8.7 AMPERES
20 VOLTS
RDS(on) = 0.03 OHM
™
D
S
CASE 751–05, Style 13
SO–8
Source
Source
Source
Gate
18
27
36
45
Top View
Drain
Drain
Drain
Drain
DEVICE MARKING
ORDERING INFORMATION
S5P02H
Device
MMSF5P02HDR2
Reel Size
13″
Tape Width
12 mm embossed tape
Quantity
4000 units
Designer’s Data for “Worst Case” Conditions — The Designer’s Data Sheet permits the design of most circuits entirely from the information presented. SOA Limit
curves — representing boundaries on device characteristics — are given to facilitate “worst case” design.
HDTMOS and MiniMOS are trademarks of Motorola, Inc. TMOS is a registered trademark of Motorola, Inc.
Preferred devices are Motorola recommended choices for future use and best overall value.
REV 2
©MMoottoororolal,aInTc.M19O9S7 Power MOSFET Transistor Device Data
1
1 page 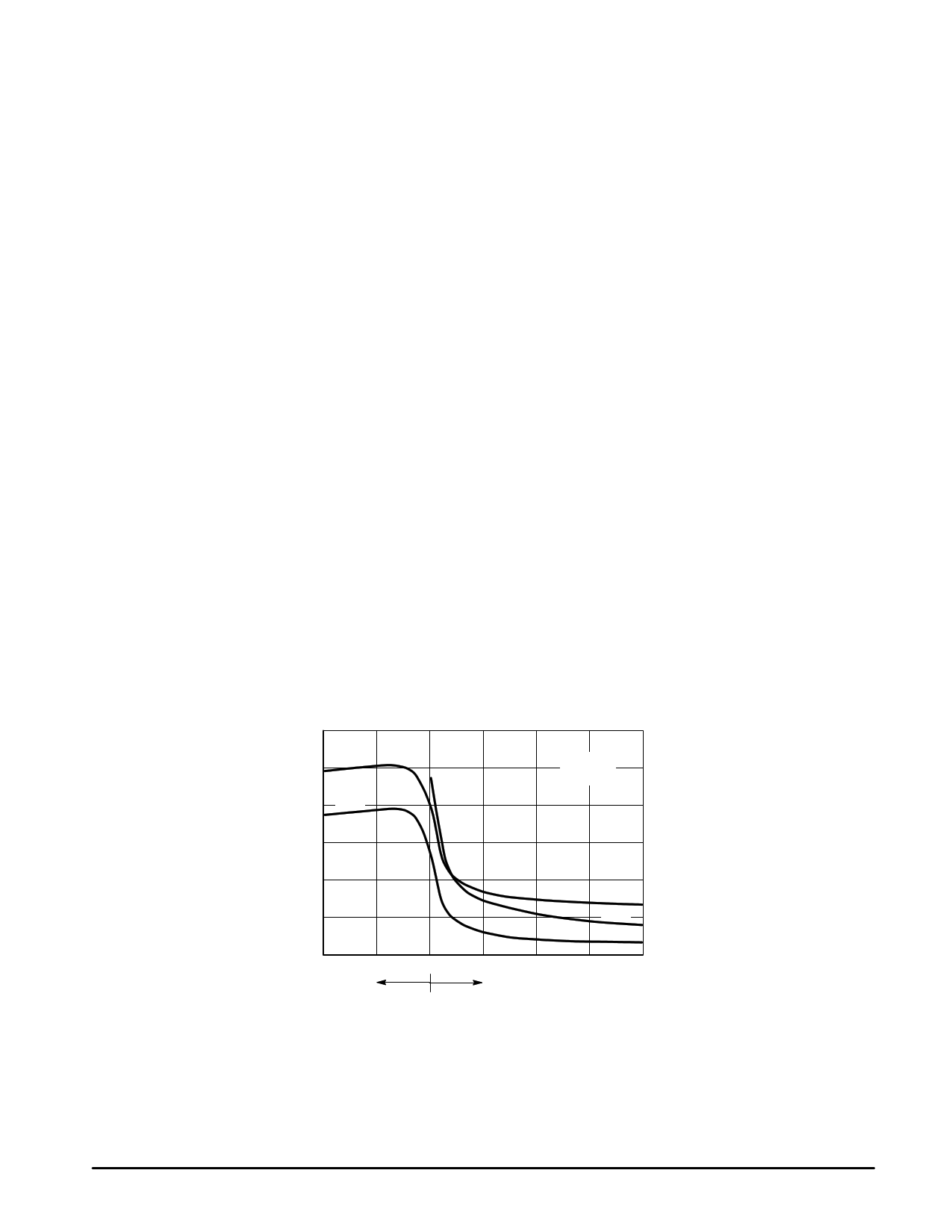
POWER MOSFET SWITCHING
MMSF5P02HD
Switching behavior is most easily modeled and predicted
by recognizing that the power MOSFET is charge controlled.
The lengths of various switching intervals (∆t) are deter-
mined by how fast the FET input capacitance can be charged
by current from the generator.
The published capacitance data is difficult to use for calculat-
ing rise and fall because drain–gate capacitance varies
greatly with applied voltage. Accordingly, gate charge data is
used. In most cases, a satisfactory estimate of average input
current (IG(AV)) can be made from a rudimentary analysis of
the drive circuit so that
t = Q/IG(AV)
During the rise and fall time interval when switching a resis-
tive load, VGS remains virtually constant at a level known as
the plateau voltage, VSGP. Therefore, rise and fall times may
be approximated by the following:
tr = Q2 x RG/(VGG – VGSP)
tf = Q2 x RG/VGSP
where
VGG = the gate drive voltage, which varies from zero to VGG
RG = the gate drive resistance
and Q2 and VGSP are read from the gate charge curve.
During the turn–on and turn–off delay times, gate current is
not constant. The simplest calculation uses appropriate val-
ues from the capacitance curves in a standard equation for
voltage change in an RC network. The equations are:
td(on) = RG Ciss In [VGG/(VGG – VGSP)]
td(off) = RG Ciss In (VGG/VGSP)
The capacitance (Ciss) is read from the capacitance curve at
a voltage corresponding to the off–state condition when cal-
culating td(on) and is read at a voltage corresponding to the
on–state when calculating td(off).
At high switching speeds, parasitic circuit elements com-
plicate the analysis. The inductance of the MOSFET source
lead, inside the package and in the circuit wiring which is
common to both the drain and gate current paths, produces a
voltage at the source which reduces the gate drive current.
The voltage is determined by Ldi/dt, but since di/dt is a func-
tion of drain current, the mathematical solution is complex.
The MOSFET output capacitance also complicates the
mathematics. And finally, MOSFETs have finite internal gate
resistance which effectively adds to the resistance of the
driving source, but the internal resistance is difficult to mea-
sure and, consequently, is not specified.
The resistive switching time variation versus gate resis-
tance (Figure 9) shows how typical switching performance is
affected by the parasitic circuit elements. If the parasitics
were not present, the slope of the curves would maintain a
value of unity regardless of the switching speed. The circuit
used to obtain the data is constructed to minimize common
inductance in the drain and gate circuit loops and is believed
readily achievable with board mounted components. Most
power electronic loads are inductive; the data in the figure is
taken with a resistive load, which approximates an optimally
snubbed inductive load. Power MOSFETs may be safely op-
erated into an inductive load; however, snubbing reduces
switching losses.
6000
Ciss
4000 Crss
TJ = 25°C
VGS = 0 V
2000
0
–10
Ciss
Coss
Crss
VGS 0 VDS
10
20
VDS, DRAIN–TO–SOURCE VOLTAGE (VOLTS)
Figure 7. Capacitance Variation
Motorola TMOS Power MOSFET Transistor Device Data
5
5 Page 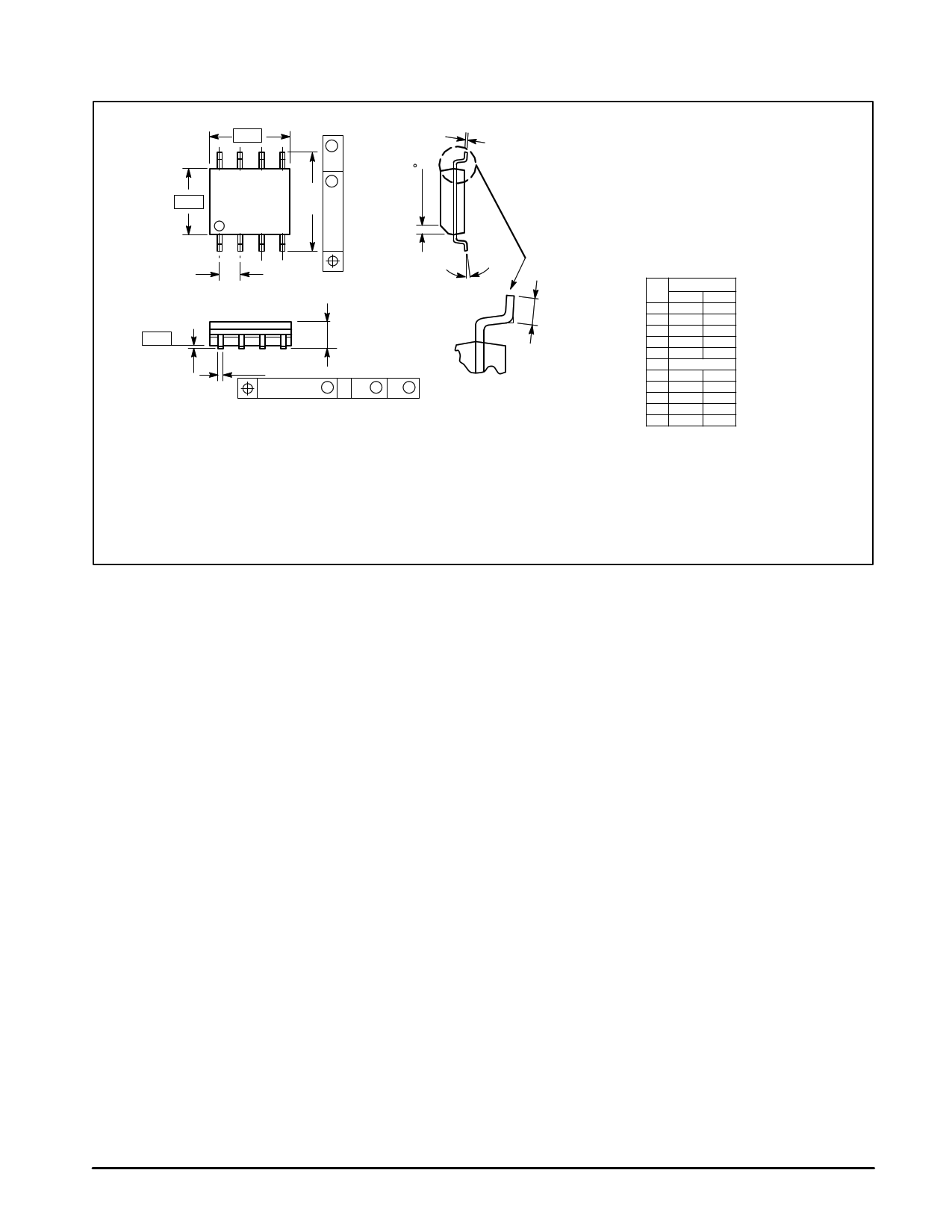
PACKAGE DIMENSIONS
MMSF5P02HD
–A–
8
–B–
1
5
4
G
J
M_
–T–
8X D
SEATING
PLANE
0.25 (0.010) M T B S A S
CASE 751–05
SO–8
ISSUE P
NOTES:
1. DIMENSIONS A AND B ARE DATUMS AND T IS A
DATUM SURFACE.
2. DIMENSIONING AND TOLERANCING PER ANSI
Y14.5M, 1982.
3. DIMENSIONS ARE IN MILLIMETER.
4. DIMENSION A AND B DO NOT INCLUDE MOLD
PROTRUSION.
5. MAXIMUM MOLD PROTRUSION 0.15 PER SIDE.
6. DIMENSION D DOES NOT INCLUDE MOLD
PROTRUSION. ALLOWABLE DAMBAR
PROTRUSION SHALL BE 0.127 TOTAL IN EXCESS
OF THE D DIMENSION AT MAXIMUM MATERIAL
CONDITION.
MILLIMETERS
DIM MIN MAX
A 4.80 5.00
B 3.80 4.00
C 1.35 1.75
D 0.35 0.49
F 0.40 1.25
G 1.27 BSC
J 0.18 0.25
K 0.10 0.25
M 0_ 7_
P 5.80 6.20
R 0.25 0.50
STYLE 13:
PIN 1. SOURCE
2. SOURCE
3. SOURCE
4. GATE
5. DRAIN
6. DRAIN
7. DRAIN
8. DRAIN
Motorola TMOS Power MOSFET Transistor Device Data
11
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 12 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet MMSF5P02HD.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| MMSF5P02HD | SINGLE TMOS POWER MOSFET 8.7 AMPERES 20 VOLTS | Motorola Semiconductors |
| MMSF5P02HD | Power MOSFET ( Transistor ) | ON Semiconductor |
| MMSF5P02HDR2 | Power MOSFET ( Transistor ) | ON Semiconductor |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |