
|
|
PDF MT46H32M32LG Data sheet ( Hoja de datos )
| Número de pieza | MT46H32M32LG | |
| Descripción | Mobile Low-Power DDR SDRAM | |
| Fabricantes | Micron Technology | |
| Logotipo |  |
|
Hay una vista previa y un enlace de descarga de MT46H32M32LG (archivo pdf) en la parte inferior de esta página. Total 30 Páginas | ||
|
No Preview Available !
1Gb: x16, x32 Mobile LPDDR SDRAM
Features
Mobile Low-Power DDR SDRAM
MT46H64M16LF – 16 Meg x 16 x 4 banks
MT46H32M32LF – 8 Meg x 32 x 4 banks
MT46H32M32LG – 8 Meg x 32 x 4 banks
Features
• VDD/VDDQ = 1.70–1.95V
• Bidirectional data strobe per byte of data (DQS)
• Internal, pipelined double data rate (DDR)
architecture; two data accesses per clock cycle
• Differential clock inputs (CK and CK#)
• Commands entered on each positive CK edge
• DQS edge-aligned with data for READs; center-
aligned with data for WRITEs
• 4 internal banks for concurrent operation
• Data masks (DM) for masking write data; one mask
per byte
• Programmable burst lengths (BL): 2, 4, 8, or 16
• Concurrent auto precharge option is supported
• Auto refresh and self refresh modes
• 1.8V LVCMOS-compatible inputs
• Temperature-compensated self refresh (TCSR)
• Partial-array self refresh (PASR)
• Deep power-down (DPD)
• Status read register (SRR)
• Selectable output drive strength (DS)
• Clock stop capability
• 64ms refresh, 32ms for automotive temperature
Table 1: Key Timing Parameters (CL = 3)
Speed Grade
-5
-54
-6
-75
Clock Rate
200 MHz
185 MHz
166 MHz
133 MHz
Access Time
5.0ns
5.0ns
5.0ns
6.0ns
Options
Marking
• VDD/VDDQ
– 1.8V/1.8V
H
• Configuration
– 64 Meg x 16 (16 Meg x 16 x 4
64M16
banks)
– 32 Meg x 32 (8 Meg x 32 x 4 banks) 32M32
• Addressing
– JEDEC-standard
LF
– JEDEC reduced page size
LG
• Plastic "green" package
– 60-ball VFBGA (8mm x 9mm)1
– 90-ball VFBGA (8mm x 13mm)2
BF
B5
• PoP (plastic "green" package)
– 168-ball WFBGA (12mm x 12mm)2
MA
• Timing – cycle time
– 5ns @ CL = 3 (200 MHz)
-5
– 5.4ns @ CL = 3 (185 MHz)
-54
– 6ns @ CL = 3 (166 MHz)
-6
– 7.5ns @ CL = 3 (133 MHz)
-75
• Power
– Standard IDD2/IDD6
• Operating temperature range
None
– Commercial (0˚ to +70˚C)
None
– Industrial (–40˚C to +85˚C)
– Automotive (–40˚C to +105˚C)3
IT
AT
• Design revision
:B
Notes:
1. Only available for x16 configuration.
2. Only available for x32 configuration.
3. Contact factory for availability.
PDF: 09005aef83d9bee4
1gb_ddr_mobile_sdram_t68m.pdf - Rev. G 9/11 EN
1 Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2009 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
Products and specifications discussed herein are subject to change by Micron without notice.
1 page 
1Gb: x16, x32 Mobile LPDDR SDRAM
Features
List of Figures
Figure 1: 1Gb Mobile LPDDR Part Numbering .................................................................................................. 2
Figure 2: Functional Block Diagram (x16) ......................................................................................................... 9
Figure 3: Functional Block Diagram (x32) ....................................................................................................... 10
Figure 4: 60-Ball VFBGA – Top View, x16 only .................................................................................................. 11
Figure 5: 90-Ball VFBGA – Top View, x32 only .................................................................................................. 12
Figure 6: 168-Ball FBGA – 12mm x 12mm (Top View), x32 only ........................................................................ 13
Figure 7: 60-Ball VFBGA (8mm x 9mm), Package Code: BF .............................................................................. 16
Figure 8: 90-Ball VFBGA (8mm x 13mm), Package Code: B5 ............................................................................. 17
Figure 9: 168-Ball WFBGA (12mm x 12mm), Package Code: MA ....................................................................... 18
Figure 10: Typical Self Refresh Current vs. Temperature .................................................................................. 28
Figure 11: ACTIVE Command ........................................................................................................................ 40
Figure 12: READ Command ........................................................................................................................... 41
Figure 13: WRITE Command ......................................................................................................................... 42
Figure 14: PRECHARGE Command ................................................................................................................ 43
Figure 15: DEEP POWER-DOWN Command ................................................................................................... 44
Figure 16: Simplified State Diagram ............................................................................................................... 50
Figure 17: Initialize and Load Mode Registers ................................................................................................. 52
Figure 18: Alternate Initialization with CKE LOW ............................................................................................ 53
Figure 19: Standard Mode Register Definition ................................................................................................. 54
Figure 20: CAS Latency .................................................................................................................................. 57
Figure 21: Extended Mode Register ................................................................................................................ 58
Figure 22: Status Read Register Timing ........................................................................................................... 60
Figure 23: Status Register Definition .............................................................................................................. 61
Figure 24: READ Burst ................................................................................................................................... 64
Figure 25: Consecutive READ Bursts .............................................................................................................. 65
Figure 26: Nonconsecutive READ Bursts ........................................................................................................ 66
Figure 27: Random Read Accesses .................................................................................................................. 67
Figure 28: Terminating a READ Burst ............................................................................................................. 68
Figure 29: READ-to-WRITE ............................................................................................................................ 69
Figure 30: READ-to-PRECHARGE .................................................................................................................. 70
Figure 31: Data Output Timing – tDQSQ, tQH, and Data Valid Window (x16) .................................................... 71
Figure 32: Data Output Timing – tDQSQ, tQH, and Data Valid Window (x32) .................................................... 72
Figure 33: Data Output Timing – tAC and tDQSCK .......................................................................................... 73
Figure 34: Data Input Timing ......................................................................................................................... 75
Figure 35: Write – DM Operation .................................................................................................................... 76
Figure 36: WRITE Burst ................................................................................................................................. 77
Figure 37: Consecutive WRITE-to-WRITE ....................................................................................................... 78
Figure 38: Nonconsecutive WRITE-to-WRITE ................................................................................................. 78
Figure 39: Random WRITE Cycles .................................................................................................................. 79
Figure 40: WRITE-to-READ – Uninterrupting ................................................................................................. 80
Figure 41: WRITE-to-READ – Interrupting ...................................................................................................... 81
Figure 42: WRITE-to-READ – Odd Number of Data, Interrupting ..................................................................... 82
Figure 43: WRITE-to-PRECHARGE – Uninterrupting ....................................................................................... 83
Figure 44: WRITE-to-PRECHARGE – Interrupting ........................................................................................... 84
Figure 45: WRITE-to-PRECHARGE – Odd Number of Data, Interrupting .......................................................... 85
Figure 46: Bank Read – With Auto Precharge ................................................................................................... 88
Figure 47: Bank Read – Without Auto Precharge .............................................................................................. 89
Figure 48: Bank Write – With Auto Precharge .................................................................................................. 90
Figure 49: Bank Write – Without Auto Precharge ............................................................................................. 91
Figure 50: Auto Refresh Mode ........................................................................................................................ 92
PDF: 09005aef83d9bee4
1gb_ddr_mobile_sdram_t68m.pdf - Rev. G 9/11 EN
5 Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2009 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
5 Page 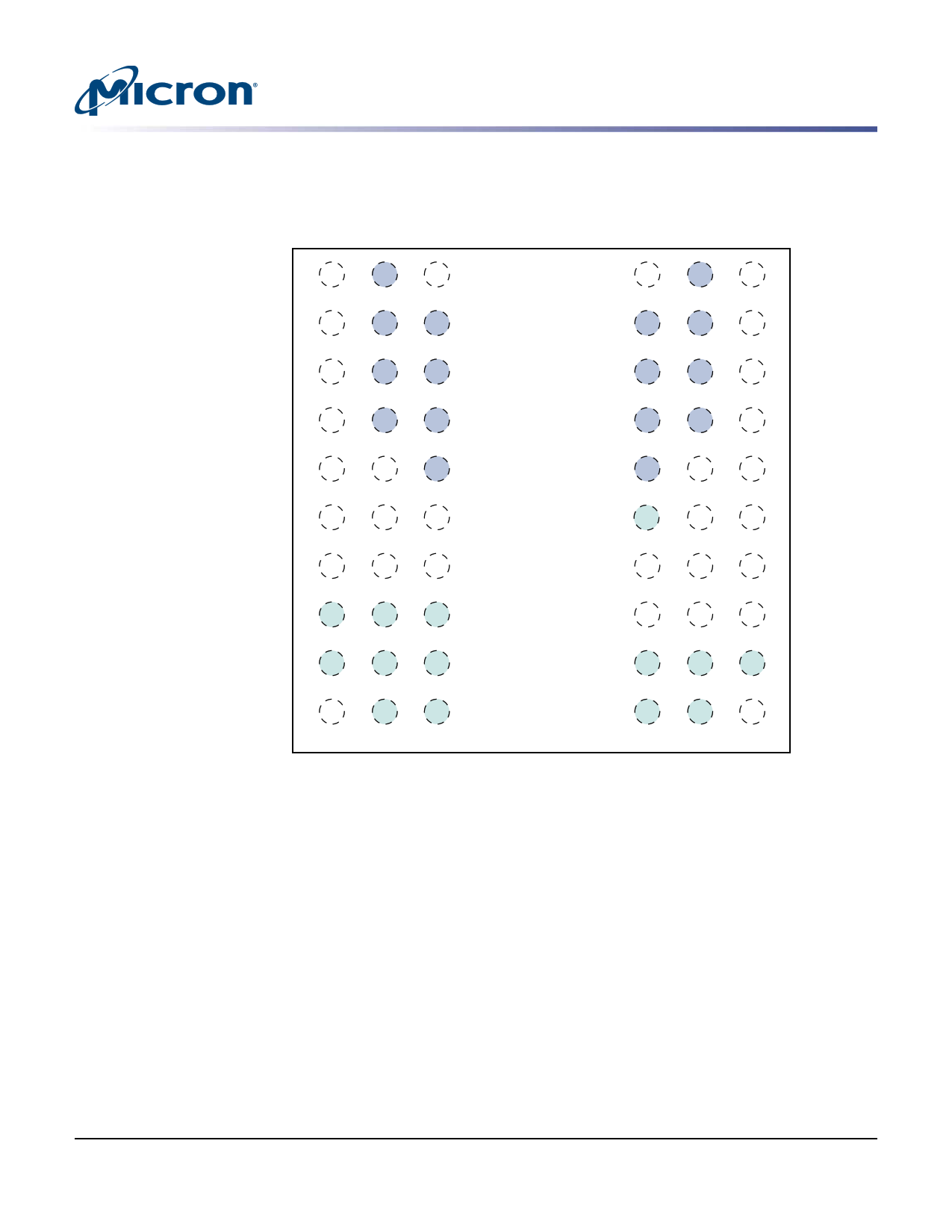
Ball Assignments and Descriptions
Figure 4: 60-Ball VFBGA – Top View, x16 only
123
4
1Gb: x16, x32 Mobile LPDDR SDRAM
Ball Assignments and Descriptions
56789
A
VSS DQ15 VSSQ
B
VDDQ DQ13 DQ14
C
VSSQ DQ11 DQ12
D
VDDQ DQ9 DQ10
E
VSSQ UDQS DQ8
F
VSS UDM NC
G
CKE CK CK#
H
A9 A11 A12
J
A6 A7 A8
K
VSS A4 A5
VDDQ DQ0
VDD
DQ1 DQ2 VSSQ
DQ3 DQ4 VDDQ
DQ5 DQ6 TEST1
DQ7 LDQS VDDQ
A13 LDM VDD
WE# CAS# RAS#
CS# BA0 BA1
A10/AP A0
A1
A2 A3 VDD
Notes: 1. D9 is a test pin that must be tied to VSS or VSSQ in normal operations.
2. Unused address pins become RFU.
PDF: 09005aef83d9bee4
1gb_ddr_mobile_sdram_t68m.pdf - Rev. G 9/11 EN
11
Micron Technology, Inc. reserves the right to change products or specifications without notice.
© 2009 Micron Technology, Inc. All rights reserved.
11 Page | ||
| Páginas | Total 30 Páginas | |
| PDF Descargar | [ Datasheet MT46H32M32LG.PDF ] | |
Hoja de datos destacado
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| MT46H32M32LF | Mobile Low-Power DDR SDRAM | Micron Technology |
| MT46H32M32LG | Mobile Low-Power DDR SDRAM | Micron Technology |
| Número de pieza | Descripción | Fabricantes |
| SLA6805M | High Voltage 3 phase Motor Driver IC. |
Sanken |
| SDC1742 | 12- and 14-Bit Hybrid Synchro / Resolver-to-Digital Converters. |
Analog Devices |
|
DataSheet.es es una pagina web que funciona como un repositorio de manuales o hoja de datos de muchos de los productos más populares, |
| DataSheet.es | 2020 | Privacy Policy | Contacto | Buscar |
